In this post, you’re going to learn the difference between rage and anger.
What Is Rage?
Rage is an intense and uncontrolled anger response that often involves a strong emotional and physiological reaction.
It typically manifests as an extreme outburst of anger, aggression, or violent behavior.
Rage can vary in intensity, duration, and triggers from person to person.
Rage can stem from various underlying factors such as unresolved anger, past trauma, frustration, or feelings of powerlessness.
What Is Anger?
Anger is a natural and fundamental human emotion that arises in response to perceived threats, injustice, frustration, or when our needs are not being met.
It is a normal emotion that everyone experiences from time to time.
Anger can manifest in various ways, ranging from mild irritation to intense rage.
Anger serves a purpose by mobilizing our energy and motivating us to take action.
It can provide a sense of power and control when we feel threatened or mistreated.
However, if anger is not expressed or managed appropriately, it can become destructive, affecting both our mental and physical well-being, as well as our relationships.
Related: Top 14 CBT Exercise For Anger Management (+FREE Anger Worksheets)
Rage vs. Anger
Rage and anger are two closely related emotions, but they differ in intensity and duration.
Anger is generally considered a less intense emotion compared to rage.
It occurs in response to perceived threats, frustration, or when our needs are not being met.
Anger can range from mild irritation to a more intense feeling of displeasure or annoyance.
It is a natural emotion that everyone experiences from time to time.
When experienced in a healthy manner, anger can serve as a motivator for change and problem-solving.
On the other hand, rage is an extreme and intense form of anger.
It involves a loss of control over one’s emotions and can lead to aggressive or destructive behavior.
Rage often manifests as an overwhelming and uncontrollable burst of anger that may be accompanied by physical or verbal outbursts, violence, or a complete disregard for consequences.
While anger can typically be managed through healthy coping strategies, rage requires greater attention and intervention.
If rage becomes a pattern or significantly impacts one’s life and relationships, it is important to seek professional help.
Related: Assertive Anger: What It Is & How to Practice It
How to Cope with Rage And Anger?
1. Identify triggers
Pay attention to situations, thoughts, or events that tend to provoke your anger.
Understanding your triggers can help you anticipate and prepare for them better.
2. Practice relaxation techniques
Deep breathing exercises, progressive muscle relaxation, and mindfulness meditation have been found to be effective in reducing anger levels and promoting emotional regulation.
The following is a breathing exercise you can try:
1. Find a quiet and comfortable place to sit or lie down.
2. Place one hand on your abdomen, just below your ribcage, and the other hand on your chest.
3. Take a slow and deep breath in through your nose, letting your abdomen rise as you inhale. Focus on filling your lungs with air, rather than your chest.
4. Exhale slowly through your mouth, allowing your abdomen to fall as you breathe out. Try to make your exhalation longer than your inhalation.
5. Continue this deep belly breathing pattern for several minutes, focusing on the sensation of your breath entering and leaving your body.
6. If your mind starts to wander, gently bring your attention back to your breath.
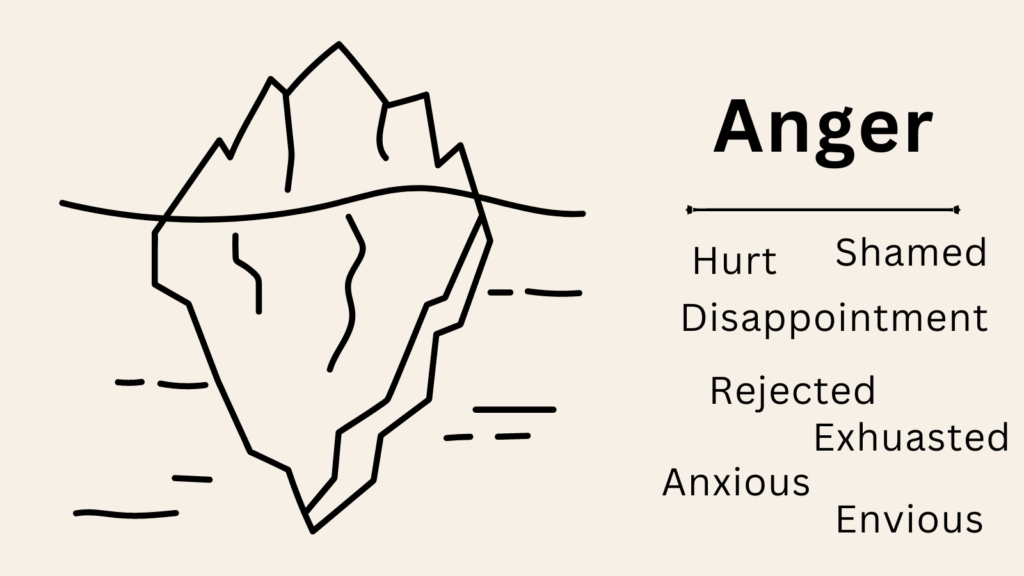
Related: Anger Iceberg: How to Use It (+FREE Anger Iceberg Worksheet PDF)
3. Use cognitive restructuring
Challenge and reframe unhelpful thoughts or beliefs that contribute to anger.
For example, try to see situations from different perspectives, consider alternative explanations, or focus on problem-solving rather than dwelling on negative emotions.
4. Develop assertiveness skills
Learn and practice assertive communication techniques to express your needs, set boundaries, and address conflicts in a constructive manner.
Assertiveness can help prevent anger from building up and escalating.
5. Engage in physical activity
Regular exercise, such as aerobic activities or sports, can help release pent-up energy and stress, promote relaxation, and improve overall mood and well-being.
Related: Best 10 Anger Management Books And Workbooks
6. Take a timeout
When you feel yourself becoming overwhelmed with rage, take a break and remove yourself from the situation temporarily.
Find a quiet space where you can calm down, reflect, and regain composure before addressing the issue.
7. Create a support network
Reach out to trusted friends, family members, or support groups who can provide understanding, empathy, and guidance during times of anger or rage.
Sharing your experiences and emotions with others can also provide a sense of validation and help you feel less alone.
Related: Top 15 Anger Journal Prompts (+FREE Worksheets)

Conclusion
It is essential to prioritize your safety and the safety of others while managing rage and anger.
If you find it challenging to control or manage your anger independently, seeking professional help is highly recommended.