In this post you’re going to learn all about window of tolerance.
What Is the Window of Tolerance?
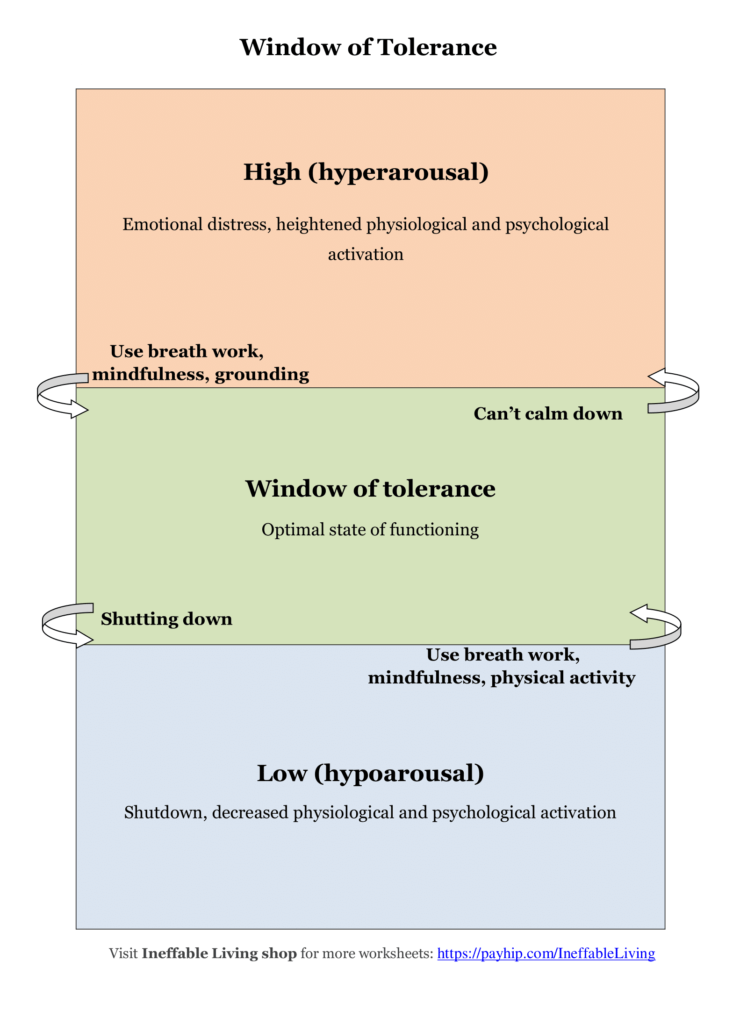
The “window of tolerance” is a term commonly used in trauma-informed therapy to describe an optimal range of emotional and physiological arousal within which an individual can effectively cope with stressors.
It represents a state where a person can handle both mild distress and moderate challenges without becoming overwhelmed or emotionally dysregulated.
When someone is within their window of tolerance, they are better able to think clearly, make decisions, engage in problem-solving, and maintain healthy relationships.
However, when stress levels increase beyond their capacity to cope, they may either shift into hyperarousal (fight-or-flight response) or hypoarousal (a dissociative or shutdown response).
Components of the Window of Tolerance
The Window of Tolerance consists of three components: optimal arousal level, hyperarousal, and hypoarousal.
1. Optimal arousal level
This refers to a balanced state of activation where individuals feel calm, focused, and capable of coping with life’s challenges.
It involves an optimal balance between the sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous systems.
When within this range, we can process information and emotions efficiently and make adaptive decisions.
2. Hyperarousal
Hyperarousal occurs when individuals experience an excessive activation of the sympathetic nervous system, commonly associated with the “fight-or-flight” response.
This state is characterized by increased heart rate, rapid breathing, heightened alertness, and intense emotions like anxiety, anger, or fear.
It can lead to feelings of overwhelm, irritability, difficulty concentrating, and hypervigilance.
3. Hypoarousal
Hypoarousal, on the other hand, is a state of decreased arousal that can happen when the parasympathetic nervous system dominates over the sympathetic system.
It is often associated with dissociation, numbness, disconnection, and a sense of being emotionally shut down or detached from one’s surroundings.
Individuals in a hypoaroused state may struggle with motivation, concentration, and feeling engaged with life.
Related: Best 11 Grounding Techniques For Dissociation
Factors Influencing the Individual’s Window of Tolerance
There are several factors that can influence an individual’s window of tolerance.
It’s important to note that these factors can vary from person to person, and it’s a dynamic concept influenced by both genetic and environmental factors.
Here are some key factors that can impact one’s window of tolerance:
1. Early life experiences
Experiences in childhood, such as trauma or neglect, can shape the development of the nervous system and impact the individual’s ability to regulate emotions.
Adverse childhood experiences can result in a narrower window of tolerance and heightened sensitivity to stressors.
2. Attachment style
The quality of early attachment relationships can influence how individuals regulate their emotions.
Secure attachments facilitate the development of emotional regulation skills, while insecure attachments may lead to difficulties in managing stress and emotions, narrowing the window of tolerance.
Related: Earned Secure Attachment: What Is It And How To Become More Securely Attached?
3. Genetic predisposition
Certain genetic factors can contribute to individual differences in emotional regulation and reactivity.
Some people may be more prone to hyperarousal or hypoarousal responses due to genetic factors.
4. Traumatic experiences
Experiencing traumatic events can significantly impact an individual’s window of tolerance.
Trauma can disrupt the nervous system’s ability to regulate arousal levels, leading to hyperarousal or hypoarousal reactions to stressors.
5. Chronic stress
Prolonged exposure to chronic stressors, such as work-related stress or ongoing relationship difficulties, can narrow the window of tolerance over time.
It can make individuals more susceptible to experiencing hyperarousal or hypoarousal responses.
6. Coping strategies and resilience
The individual’s repertoire of coping strategies and their level of resilience can influence their capacity to tolerate distress and regulate emotions effectively.
Building resilient coping mechanisms through therapy and self-care practices can help expand the window of tolerance.
Related: How Resilience Works? Top 10 Powerful Ways to Stay Healthy and Happy During Tough Times
Techniques for Regulating the Window of Tolerance
1. Deep breathing exercises
Deep breathing exercises are a powerful technique for regulating the window of tolerance, which refers to our optimal range of arousal and emotional states.
When we are in this window, we are better able to handle stressors and challenges effectively.
Deep breathing exercises involve taking slow, deliberate breaths, focusing on inhaling and exhaling deeply.
This practice activates the parasympathetic nervous system, promoting relaxation and reducing stress levels.
It can help us return to a state of calm when we feel overwhelmed or anxious.
One example of deep breathing exercise is belly breathing, where we take slow breaths, allowing our abdomen to rise with each inhale and fall with each exhale.
2. Body scan meditation
Body scan meditation involves bringing focused attention to each part of the body, observing any sensations or tensions without judgment.
This mindfulness practice allows individuals to become more attuned to their bodily experiences, which can help regulate the window of tolerance by increasing self-awareness and allowing for a deeper connection with present moment sensations.
For example, during a body scan, one might notice areas of tightness or discomfort in the body, such as tension in the shoulders or butterflies in the stomach.
By acknowledging and accepting these sensations without judgment, individuals can learn to regulate their emotional states and cultivate a sense of calmness and relaxation.
Additionally, body scan meditation can also assist in identifying patterns of stress or discomfort in specific areas of the body, helping individuals gain insight into the impact of emotions and thoughts on their physical well-being.
Related: Best 6 Mindfulness Exercises For Beginners (+FREE Resources)
3. Grounding techniques
Grounding involves focusing on the present moment and connecting with one’s surroundings.
This technique helps individuals feel more anchored and secure, especially during periods of distress or anxiety.
Physical grounding techniques, like touching objects or engaging in tactile activities, can help redirect attention away from distressing thoughts and towards the present reality.
For example, rubbing a smooth stone or squeezing a stress ball can be calming and provide a sense of security.
4. Identifying and expressing emotions
By cultivating this ability, we can develop a deeper understanding of our emotional states and begin to recognize patterns and triggers.
Journaling can be a helpful tool for identifying and expressing emotions.
This practice allows us to explore our thoughts and feelings in a safe and private space, enabling us to gain clarity and insight. It can also serve as a form of self-expression, allowing us to articulate emotions that may otherwise go unacknowledged.
Another technique worth exploring is expressive arts therapy, which encourages the use of creative outlets such as painting, writing, or dancing to express and process emotions.
These activities can provide a non-verbal means of communication and can be particularly beneficial for individuals who struggle to put their emotions into words.
Related: Best 8 Mindfulness Exercises For Adults That Will Help You Regulate Your Emotions
5. Seeking support from trusted individuals
Seeking support from trusted individuals is a valuable technique that can help in effectively managing one’s emotions and expanding the window of tolerance.
Trusted individuals can be friends, family members, therapists, or mentors who provide a safe and non-judgmental space to express feelings and concerns.
When we reach out to trusted individuals for support, we create an opportunity to share our experiences and gain insights from someone who cares about our well-being.
They can listen attentively, provide empathy, and offer guidance or advice when needed.
For example, talking to a friend about a challenging situation at work can help us process our emotions and gain different perspectives on how to address the issue.
Similarly, seeking support from a therapist during times of distress can help us explore underlying emotions, develop coping strategies, and work towards personal growth.
6. Establishing healthy boundaries
Establishing healthy boundaries involves defining and communicating limits to ensure one’s emotional well-being and maintain healthy relationships with others.
Setting boundaries can vary depending on the context and personal preferences, but some common examples include stating one’s needs, expressing personal values, and being assertive while respecting others.
For instance, in a work setting, setting boundaries may involve clearly defining working hours, workload expectations, or personal free time.
In personal relationships, it could mean expressing one’s emotional needs and establishing what is acceptable behavior.
By establishing healthy boundaries, individuals can create a safe and comfortable environment that promotes emotional balance and reduces stress levels.
It also helps prevent burnout, fosters self-respect, and nurtures healthy connections with others.
Remember, setting boundaries is not selfish or rude; it is a necessary act of self-care that ultimately benefits both oneself and those with whom we interact.
Related: Top 25 Tips On How To Set Boundaries In A Toxic Relationship? (+FREE Worksheets PDF)
7. Promoting self-care practices
Engaging in activities that promote relaxation and rejuvenation helps individuals replenish their energy and reduce stress levels.
This can include activities such as taking warm baths, practicing yoga or deep breathing exercises, engaging in creative pursuits, or spending time in nature.
By prioritizing self-care practices, individuals can prevent their window of tolerance from narrowing and ensure they have sufficient resources to cope with stressors.
It is important to note that these suggestions may vary depending on an individual’s specific circumstances and the severity of their symptoms.
Consulting with a licensed mental health professional can provide personalized guidance tailored to your needs.
FREE Window of Tolerance PDF
Conclusion
The Window of Tolerance is a concept often used in the field of mental health to describe an optimal state of arousal in which an individual is able to effectively cope with and respond to stressors.
It represents the range of emotional and physiological states within which a person can function comfortably and engage in daily activities.
When individuals are within their window of tolerance, they are more likely to be able to handle challenges and regulate their emotions appropriately.
However, when someone’s level of arousal exceeds their window of tolerance, they may experience symptoms such as panic, anxiety, or anger, and their ability to think clearly and problem-solve can be compromised.
Developing self-awareness and learning strategies to expand one’s window of tolerance can be helpful in managing stress and improving overall well-being.